Introduction to groundnut oil extraction
Among the edible oils, groundnut oil is a widely preferred oil with good flavor, nutrition, and utility as a cooking medium. Extraction of groundnut oil follows specific stages, whereby maximum quantities and quality is obtained. In this article, we focus on the details of the groundnut oil extraction process including the preparation of the seeds and refining of the oil. The processes involved in the extraction of groundnut oil are processes that have been well detailed in different documents and this greatly helps in ensuring that all the steps are foolproof so that maximum yield and quality is achieved.
Overview of groundnut oil extraction Process
How to extract oil from groundnut?
There are two broad methods of extracting groundnut oil. They are: mechanical pressing and solvent extraction. Mechanical pressing is the oldest technique and it uses only force to extract the oil. In the case of the solvent extraction technique, chemicals are dissolved in the solvent so that more oil is extracted (chemical extraction of groundnut oil). Each of these has its own associated processes and machineries which is considerable as the norm with any extraction methods.
Key Steps in Groundnut Oil Extraction
The extraction process can be divided into several vital key parts as specified below:
- Preparation of Seeds
- Pressing of Seeds
- Refining of the oil
Every key stage contains its own set of activities or sub steps which cumulatively promote the efficiency as well as the quality of the oil obtained from the extraction processes.
1] Seed Preparation
Getting the seed ready is an integral aspect of ensuring high yields in both the quantity and quality of oil produced. This stage consists of a number of processes:
1. Cleaning
The initial process is the cleaning of groundnuts which consists of the clearance of stones, dirt, rotten seeds, etc. This is usually achieved by the use of:
- Magnetic selectors: These are utilized for the removal of any metal contamination present in the nuts.
- Cleaning sieves: For the size classification of nuts to remove any foreign materials that might be in the nuts.
- Destoners: They are used to clean up nuts by removing stones and other materials that are of the same density.
A proper cleaning at this stage prevents any risk of contamination during extraction and enhances the quality of the final product.
2. Dehulling (Shelling)
This includes the process of breaking groundnuts which is otherwise termed as de-hulling. This is done using the following tools:
- Mechanical shellers: De-hulling is essential but not indispensable since the oil pressing activity becomes straining if any shell is left since the shell has no oil content and may reduce the output otherwise.
De-hulling is essential but not indispensable since the oil pressing activity becomes straining if any shell is left since the shell has no oil content and may reduce the output otherwise.
3. Grinding or Flaking
The second stage is grinding or flaking the kernels after the dehulling process which was previously outlined. The grinding or flaking of the kernels diminishes their size which maximizes the surface area available increasing the volume of oil extraction. The most frequently employed techniques are:
- Hammer mills: This is applied to get the smaller kernels from the larger ones.
- Flaking machines: These mash the already ground kernels to a very smooth degree so that flakes can be formed for easy passage of oil during pressing.
4. Cooking (Conditioning)
Moisture and temperature content of the groundnut and its flakes can be easily made heat and oil conducive with the aid of cooking or conditioning. Undermost conditions:
- Moisture content: 5 – 7%
- Temperature: 110- 115°C
This stage aids in augmenting the plasticity; it does so by leaching out the cell walls thereby facilitating the outflow of oil during the process of pressing.
2] Pressing
This stage helps in increasing the plasticity, it does so through leaching of the cell walls which facilitates the out flow of the oil in the course of pressing.
1. Mechanical Pressing
Mechanical pressing uses either a screw or hydraulic press which exerts pressure on the groundnuts. Among other steps the following are most important:
- Using a screw press: Groundnut cake, which has been presses, is loaded into the screw press for oil extraction after it has been crushed into flakes.
- Excess pressing: with the increasing temperature due to friction and consequently building up of pressure, oil gushes out very rapidly due to its reduced viscosity.
Approximately, a rough estimate suggests that about 85% of the oil can be extracted from the groundnuts through mechanical pressing with the remaining oil, approximately a quarter, still housed within the pressed cake.
2. Solvent extraction of groundnut oil
Furthermore, to the oil press cake, a mixture may be subjected to the cake press for extraction of oil cake, and then solvent extraction: This method employs the use of certain organic solvents in the extraction of oil from oil cakes.
- Hexane or other solvents: In chemical extraction of groundnut oil these chemicals are used to dissolve the remaining last residual oil from the cake.
- Separation process: The mixture is finally processed for the removal of solvent from the resultant oil.
This method can increase total oil yield considerably but care should be taken in its application as well as operation as it employs the use of solvents which are associated with safety concerns.
3] Refining of extracted groundnut oil
The groundnut crude oil is then treated in order to clean some impurities which can be considered as non desirable for commerce in edible oil. Some of the steps in the refining process include: degumming washing, neutralization, bleaching, and deodorizing.
1. Degumming
Degumming is done on crude oil by applying hydrous or aqueous acid in order to remove phospholipids and other water soluble impurities.
2. Neutralization
The sodium hydroxide addition during the thermal treatment of the degummed oils neutralizes free fatty acids which are believed to have influence on flavor and stability.
3. Bleaching
Carbon activated or free fatty acids is what augments the quantity of odor and flavor molecules and also diminishes color pigments and some residual particles with the raw materials may contain.
4. Deodorization
Deodorization is achieved by use of heat and a vacuum for steam distillation so that the required odor and flavor attached to certain unwanted volatile particles gets vaporized from the mixture in the process.
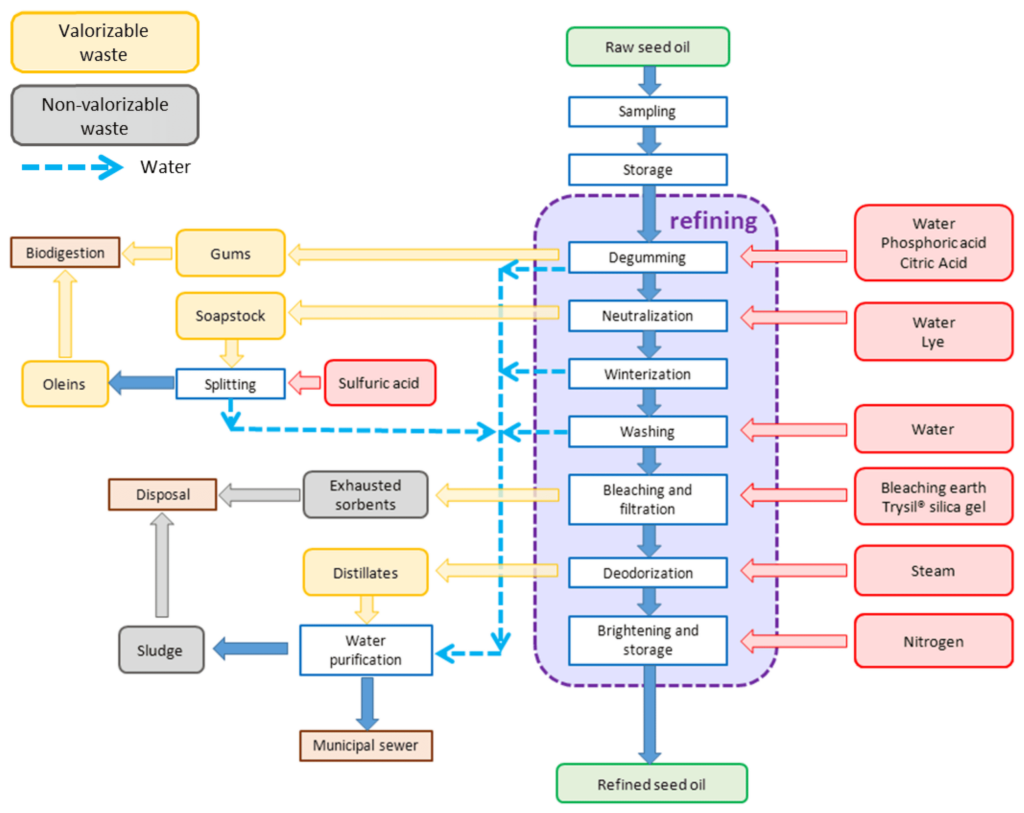
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons (www.mdpi.com)
Quality Control
At all times during the three stages of dehulling, oil extraction and refining groundnut oil, production quality control becomes a concern for consumers. The aspects of oil testing such as fatty acid composition, peroxide value, and sensory evaluation are a fair business principle in this industry.
How much oil can be extracted from 1 kg groundnut?
Oil extraction from groundnuts (peanuts) stands out in the edible oil industry especially where groundnuts are grown. Cultivators, consumers, and marketplaces dealing with the such oil need to know the yield per ton of groundnuts oil. This descriptive article will detail the extraction yield from groundnuts, the yields obtained from these methods, and oil content.
Oil Yield from groundnuts (Groundnut oil extraction percentage)
General Yield estimates
The oil present in the groundnuts varies depending on various factors which include the extraction method and the quality of the peanuts. Owing to the domains of weight, groundnuts have approximately 44 percent to 50 percent oil. Therefore from one kilogram of groundnut kernels one should expect to obtain roughly between 440 to 500 grams of oil.
Extraction Methods
The % yield (groundnut oil extraction percentage) is highly influenced by the method employed:
1. Mechanical Pressing (Expeller Pressing):
- It is a common method and consists of a mechanical press, which crushes the groundnuts.
- In most cases, 85% of oil present in the kernels is recovered.
- For instance, groundnut with 48% oil content and oil yield of 1kg can roughly extract the following:
Oil Yield=1 kg×0.48 oil content ×0.85 extraction efficiency =0.408 kg or 408 grams
2. Solvent Extraction:
- This employs the use of solvents like hexane which enables one to completely extract oil from the groundnuts.
- Almost 99% of the oil contained in the groundnuts, is extracted using the above method.
- Using the same example of 1 kg of groundnut kernels with 48% oil content:
Oil Yield=1 kg×0.48×0.99=0.4752 kg or 475.2 grams - The left oil in the cake which is left after solvent extraction is normally between 0.5% 0.7%.
Example Calculations
To summarize, here are some yield estimates based on different methods:
| Method | Oil Content (%) | Extraction Efficiency (%) | Oil Yield (grams per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Pressing | 48 | 85 | ~408 |
| Solvent Extraction | 48 | 99 | ~475 |
Factors influencing Oil Yield (Groundnut oil extraction percentage)
Amount of oil obtained from groundnuts is influenced by a number of factors:
1. Quality of Groundnuts:
- Oil content is affected by genetics, the conditions under which the plants are cultivated, and maturity during the time of harvest.
- Higher quality groundnuts generally have a higher oil content.
2. Processing Conditions:
- Oil yield may be affected by temperature and relative humidity during processing.
- Use of proper conditioning (heating and adjusting moisture content) prior to pressing helps increase oil extractability.
3. Extraction Technology:
- The yields obtained therefore would greatly depend on the kind of machinery used such as the screw presses versus the hydraulic presses.
- Recent technologies like cold pressing and supercritical CO2 extraction would also result different yields than what is obtained.
4. Pre-Processing Techniques:
- Dehulling and grinding of nuts enhance extraction owing to the increased surface area exposures.
- Shells and other undesired materials if removed before extracting oil will assist in improving the yield.
Economic considerations
It is important for producers to grasp the economics of groundnut oil production:
- As has been mentioned, it takes about 2.5 kilograms of groundnut kernels for 1 liter of oil, which can be roughly stated as about 400-500 grams of oil from a kilogram according to the extraction method employed.
- The expense factors for the producers are the purchase cost, the operational cost of conversion and the revenue that is generated from the sale of by products like pressed cake.

Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons (Thamizhpparithi Maari)
Cost Breakdown Example
Let us suppose it takes approximately 2.5 kg of ground nuts that are about Rs 90 a kg in order to bring forth a liter of oil;
- Purchasing cost for 2.5kg: 2.5×90= Rs.225
- Other costs like (manufacturing & packaging): estimated about 50Rs. & 10Rs. = 60Rs.
- Total cost per liter: Rs.225+Rs.60=Rs.285
This type of cost structure really emphasizes that producers have to keep costs under control and at the same time assure good quality in their products.
To summarize, the oil yield from groundnuts is paramount as an approximate kg of oil can be extracted which varies by extraction methods & quality of the seeds between 440 to 500 grams a kg. Mechanical pressing, in numerous instances, fails to reach the same volumetric yield as solvent extraction though it is favored because of its ease of use and lower overall operation costs.
In order to be sustainable in a competitive environment, producers have to take care of not only the technical considerations related to extraction but also the economic impacts of their procedures. With this context and knowledge, those involved with groundnut oil have a better understanding of the issues of production methods and pricing decisions.
How to extract groundnut oil at home?
Making groundnut oil from the comforts of your home is an amazing experience because you do not have to worry about any preservatives or additives in the oil. The following is the most simple yet effective way to extract groundnut oil along with simple tools easily available in most of the households, so put on your aprons and let’s get started.
Step-by-Step Process for Extracting Groundnut Oil at Home
1. Gather Your Ingredients and Tools
Ingredients:
- Groundnuts or peanuts, preferably 1 kg, which will provide you with a good yield.
Tools:
- An oven or frying pan to roast the peanuts
- A blender or grinder
- A muslin or cheese cloth or a fine mesh strain which will be used as a filter
- A container that will be used to hold the oil
2. Roasting the Groundnuts
Roasting the peanuts will provide a stronger taste to the oil and also will ensure stronger oil extraction. The following will further highlight the process. Here’s how to do it:
- Dry Roast: Making sure that the pan is at medium heat first use unroasted peanuts and place them in the pan. Continuously stir or toss the peanuts to avoid any burning. You may take them off the stove after 10 to 15 minutes when they are light brown in color and emit a pleasant aroma.
- Oven Roasting: If you don’t prefer to dry roast them in a frying pan, you can place the peanuts in the oven at 180 degrees Celsius for about 10 to 12 minutes, however you need to keep an eye on the time so that they do not get over-roasted and dried out.
3. Cooling and De-shelling
The skin is rubbed off since the skin is waste and does not have any oil content and may spoil the quality of the oil. Once it is cooled, hands are rubbed to and clean cloth to remove the outer skins by hand.
4. Grinding into Paste
You might even use a little water for uniformity but keep the water content as less as possible since this would water down the oil in the end. This can then be put into a hand grinder or a blender so that it turns into a fine paste.
5. Extracting the Oil
The paste from earlier can be used to extract oil through two different processes but in the end the outcome will be a fine oil suited up for various cooking purposes.
Method A: Manual Extraction
- Kneading: This is the process in which the paste is turned into an oil by placing the paste into a bowl and then starting to knead it with both hands for 10-15 minutes.
- Adding Water: We then slowly incorporate warm water drops into the kneading process since that would separate the oil through.
- Collecting Oil: From this oily paste, oil would gurgle to the top portion thanks to kneading and before long a sufficient measurement of oil would be inside the container with plenty to spare.
Method B: Filtering
- Using a Muslin Cloth: Take the paste that is prepared as dough and put it into a muslin cloth or a fine strainer placed on top of a bowl.
- Squeezing: Gather the cloth and twist it tightly to squeeze with force from the stick to remove glue from paste that oil as much as possible out of it.
- Collecting Oil: The cloth will hold the solid substances and the oil will flow into the bowl which is kept underneath it.
6. Storing the Oil
You are supposed to pour the oil into sterilized glass bottles or jars once it has been filtered. When they are not in use, seal the jars and store them in a cold and dark location for protection and preservation.
7. Using leftover peanut cake
The left over peanut cake (which is basically the solid remnant after oil has been extracted) can serve as an ingredient in some recipes including snacks or be added to protein smoothies.
Tips for Successful Oil Extraction
- Quality of Groundnuts: To improve output and tasting peanut oil, use groundnuts that are fresh and high quality.
- Temperature Control: When roasting, avoid using a high temperature, as that will cause the peanuts to burn, which will make your oil come out bitter.
- Kneading Technique: Do not rush in this stage, kneading is an important step in this process, and all the oil will be successfully taken out.
- Hygiene: All instruments and containers used must be clean, so that no contamination is encountered.
It is practically possible to get groundnut oil at home with the help of kitchen items. When following these steps, you will only have to savor pure homemade groundnut oil which does not contain any additives or preservatives, thus making your cooking experiences much more delicious and nutritious.
Types of groundnut oil extraction machine
Groundnut oil extraction machines are one of the equipment used for obtaining oil from groundnuts (peanuts) through cold pressing or expelling and powered oil extraction. There are several types such as oil extraction press, hydraulic oil expeller, mini oil mill, and automatic nut oil expeller. The machines come in different capacity, power and operational features to meet varying production requirements.
Groundnut oil extraction machine types and description
1. Cold Press Machines:
- Operation: The preservation of flavor and nutritional value of oil enriched in aroma and quality adds to its natural appeal thus oil is extracted not over higher temperatures.
- Capacity: They are classified mainly in models which varies from 10 kilograms to 5 tons a day.
- Power: Depending with size of operation, between 3 and 20 HP is sufficient.
- Examples: The capacity of the Rotary Cold Oil Press Machine goes up to 5 tons/day whereas smaller varieties are used for household purpose for around 10-12 kg.
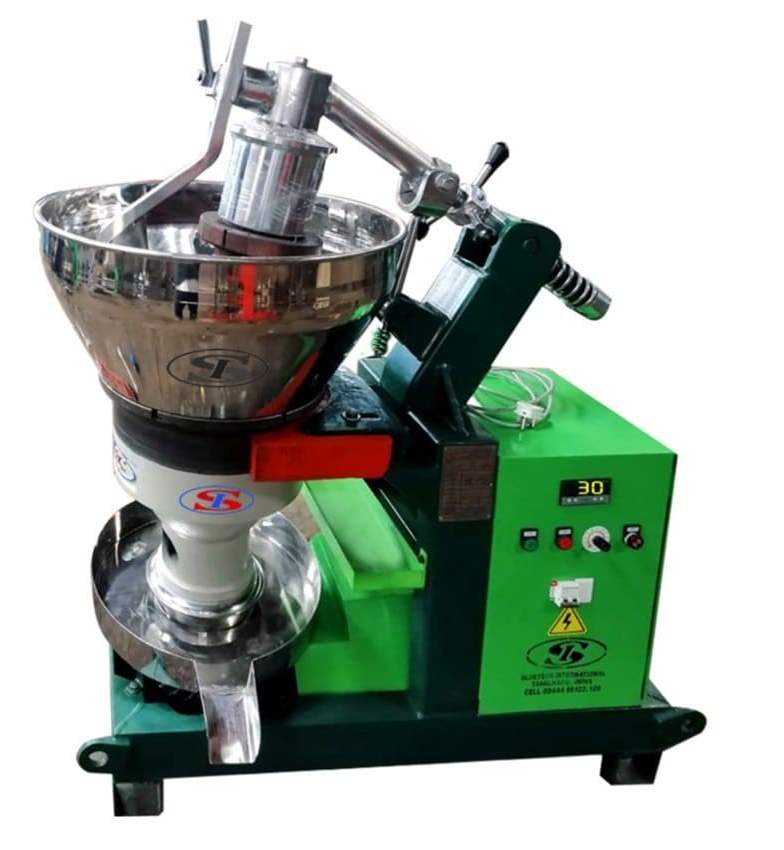

Image Credit: Indiamart.com (Bluetech International)
2. Commercial Expeller Machines:
- Operation: These Machines create the pressure in order to extract the oil and most of the times do this at high temperatures instead of using cold pressing methods.
- Capacity: Has the ability to function from 1 ton to 15 tons per day, which is good for bigger operations.
- Power: Usually falls in the range of 12.5 HP to 50 HP.
- Features: A lot of models tend to have the cooking kettles and the filter presses in them which helps to improve the overall efficiency and quality of the oil.
3. Semi Automatic Machines:
- These machines are good for small and medium sized businesses as they are neither fully manual nor fully automatic.
- They are also easier to handle with lower capacity eg: 50-300 kg/day.
Key Features
- Material Construction: In order for the machine to be long lasting and hygienic in most cases the machines are built using Mild Steel (MS) or Stainless Aluminium (SA).
- Automation Grade: Has a large selection of manual or fully automatic systems depending on the need of the user.
- Maintenance: It was built for easy washing and cleaning which is important for the coding so that the quality of the oil produced is maintained.
The procedure of producing edible oil is made easier by the use of the groundnut oil extraction machines, which provide a variety of solutions depending on the scale of operations. These machines enable extraction of oil more effectively without compromising on the quality of groundnut oil whether it is in a small home based business or a large scale business.
Some popular High Quality best groundnut for oil extraction
Here are certain salient features concerning the best groundnut varieties for oil extraction:
- Somnath: A good groundnut variety for oil extraction as it contains more than 49% oil as well as good taste. Also used for making good quality of peanut butter further proving the quality of the oil extraction.
- Girnar-4 and Girnar-5: These high-oleic groundnut varieties have oleic acid content of 78.9 % to 80.7 % and could be used to make super grade peanut oil. High oleic acid levels help to enhance the oxidative stability and oil shelf life.
- GG6: This groundnut cultivar produces an abundance of oil (about 51.1%) and can therefore be used to extract oil and make peanut butter.
- ICGV37: This is also good in oil extraction with a good amount of oil approximately 50.1%.
- Pod Yield: Both the Girnars have performed very well in pod yields of 2309–4462 kg/ha which is good for maximizing oil outputs per hectare.
- Nutritional Benefits: A highly proteinaceous crop with a plethora of other nutrients that are useful not only for producing oil but more so for other food products.
These varieties are suggested on the basis of their oil percentage content, taste and overall characteristics for suitability in oil extraction and therefore considering domestic or industrial production for groundnut oil.
Must Read,
✔️ What is the Difference Between Kullakar Rice and Poongar Rice?
✔️ Rice Mill Business: Starting a Rice Mill in India
Conclusion
The extraction of oil from the groundnut involves a number of steps that are interrelated and dependent on each other to achieve high volume of oil. The oil is extracted after proper treatment of seeds through mechanical or chemical aid and then refinement of oil, each of the steps is critical as the oil is one of the most important and widely consumed oils across the countries.
These processes also explain the sophistication that is available of the technology that is used in the retrieval of oil from groundnuts while at the same time showing how important quality control is so that safe and healthy foods may be given to the people from different parts of the globe. As groundnut oil becomes more popular better ways to extract the oil and improved machinery will be introduced to assist in tackling the challenges faced thus increasing the oil production.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which groundnut variety has the highest oil content?
Gujarat Junagadh Groundnut 32 (GJG 32) is reported to have the maximum oil content of 53.9 %. This variety not only has a good oil yield but is also able to resist several diseases which makes it possible to be grown in various agro climatic zones including Gujarat during kharif.
Are there any groundnut varieties specifically suited for cold-pressing oil?
Girnar-4 and Girnar-5 are very well adapted for oil extraction through cold-pressing. The high oleic varieties have oleic content of 78.9%-80.7%, which increases the oxidative stability and shelf life of the oil. They have favorable fatty acid composition which helps in the production of high grade cold pressed groundnut oil, which is more nutritious and flavored than oils extracted by other processes.
What is the ideal O/L ratio for maximizing the shelf-life of groundnut oil?
The ideal oleic to linoleic (O/L) ratio for enhancing the shelf-life of groundnut oil surpasses the 10:1 limits. High levels of O/L significantly increases the ratio of muscle oil and flavor of the oil thereby increasing its longevity to as high as ten fold compared to the average O/L ratio of about 1.5:1. This ratio considerably helps in minimizing oxidation and rancid formation thus making high-oleic types of groundnut more suitable for oil extraction.
How does the iodine value correlate with the shelf-life of groundnut oil?
The iodine value (IV) index is among the first few ones, which indicate the level of unsaturation in oils, and along with it, the more the reduction in IV values, the better the shelf life and stability of the oil. Low iodine value groundnut oils contain high oleic acid and low linoleic acid which are characterized by higher oxidative stability. As a result, those oils that have low iodine value are less likely to become rancid and are likely to last longer than others.
What are the health benefits of high oleic acid content in groundnut oil?
Groundnut oil with elevated oleic acid content has many health advantages since it is able to help in increasing good cholesterol (HDL) while reducing the impaired cholesterol (LDL) thereby contributing to better heart health. Furthermore, oleic acid has been found to have anti inflammatory effects and may help prevent heart diseases. Their stability further implies that high oleic oils can be made use of for cooking since they do not generate dangerous substances.
How does the oxidation rate of oleic acid compare to linoleic acid in groundnut oil?
Oleic acid is 10 to 40 times more stable than linoleic acid and hence is less likely to undergo oxidation. This also gives high oleic acid oils a longer shelf life as they are less likely to develop off-flavors or become rancid when exposed to heat or oxygen during cooking and storage.
What are the environmental factors that affect the oleic acid content in groundnuts?
Temperature, amount of moisture, type of soil, and agricultural practices are environmental factors that can have a major impact on the quantity of oleic acid content in groundnuts. For example, weather conditions, specifically elevating temperature in the growing season, promotes oleic acid however, soil nutrient variations also alter fatty acid profiles. Hence a good amount of oleic acid in groundnut varieties is achievable through proper irrigation and farming techniques.
How does the iodine value influence the nutritional quality of groundnut oil?
The IV of groundnut also oil indicates the level of unsaturation of its fatty acids. From the perspective of heart health and cholesterol reduction, it is usually ideal to have a high iodine value since this signifies a high amount of unsaturated fats. However, it must be noted that very high iodine values may also reflect the foods instability and low shelf life because they are very likely to oxidize readily. Therefore, the adequacy of the iodine value which takes of about the ranges (groundnut oil usually has an iodine value between 85 and 99) is very important in determining both nutritional quality and stability of the oil.
What are the common methods to measure the O/L ratio in groundnut oil?
Determination of oleic to linoleic (O/L) ratio in groundnut oil with the help of gas chromatography which enables the separation and determination of the various fatty acids present in the oil. Another method consists of computing the O/L ratio from the oil composition determined by the titration methods which enable the determination of the iodine value and the percentage of fatty acids. In particular, an O/L ratio can be calculated using the following formula:
O/L Ratio = % Linoleic Acid / % Oleic Acid
This to a great extent determines the stability of the oil and health aspects of the oil in regards to consumption.
How does refining process alter the iodine value of groundnut oil?
The crude oil iodine value of approximately 91mg/100g drops to above 86mg/100g during the refining process of groundnut oil suggesting a lower level of unsaturation of the oil whereby its degree of refining with maturity in oxidative conditions and heat treatment throughout refining. Although the loss is not great this implies that refining possesses the relative ability to change the composition of the oil for the better because it would bear more unsaturated fatty acids which are more reactive and also make the oil more stable hence longer shelf life.









